Insurance 101: Proteksyon laban sa financial loss
Many Filipinos are still hesitant pagdating sa usapang insurance. Some believe it’s an additional expense na hindi mapapakinabangan. Others avoid talking about death and illness dahil malas daw ito.
Sadly, nagdadala ng kahirapan sa maraming Pinoy ang ganitong attitude. 1.5 million Filipino households are pushed into poverty every year dahil sa di-inaasahang medical expenses. Napipilitan silang magbayad out-of-pocket o mangutang for emergencies.
Para makaiwas sa sitwasyong ito, it’s best to be insured. Insurance is a contract na nagbibigay ng cash assistance sayo in case of accidents, damages, or loss. With this reimbursement, hindi ka mapapagastos at magpa-panic just to cover your expenses. This gives you peace of mind and security.
Insurance is also an investment in financial security. Nag-i-invest ka ng pera for your future so you can survive any financial setback. Read on to know how to protect yourself with this financial tool!

What you’ll learn
- Important terms to know
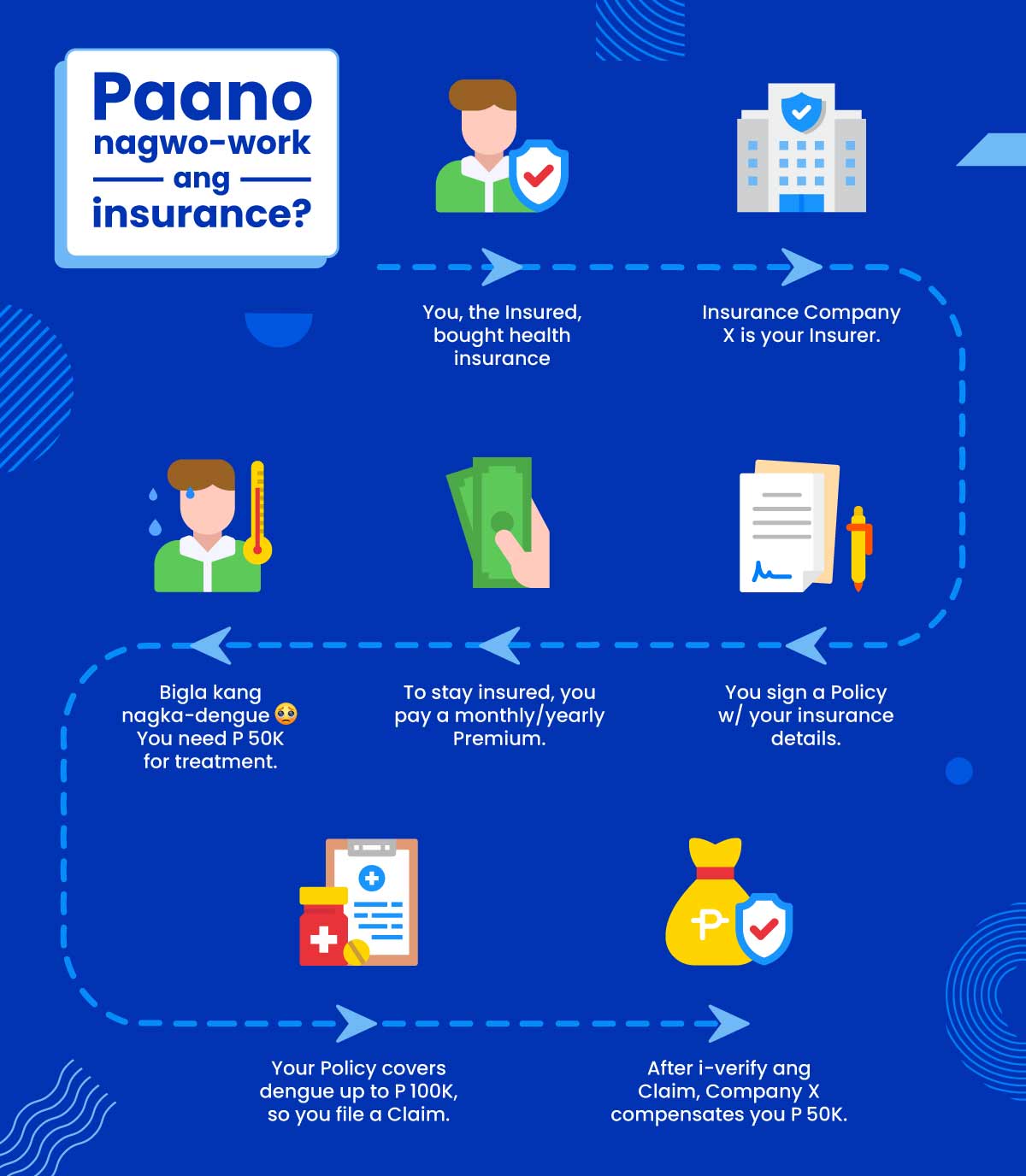
- Paano nagwo-work ang insurance?
- Different types
- How to apply
- Which insurance should you get first?
- Best practices in choosing insurance
Important terms to know
Policy. Ang official contract between the policyholder and the insurer. Narito ang terms ng inyong agreement regarding coverage, payments, conditions, limits, and more.
Policyholder. Ang registered owner ng policy. Depending on your insurance, the policyholder may or may not be the insured.
For example: Kumuha ka ng education insurance for your son. Ikaw ang policyholder, while your son is the insured.
Insured. Ang inaalagaan ng insurance. It can be you, your family, or your assets.
Insurer. Ang company na magbibigay ng coverage sa insured.
Beneficiary. This often applies to life insurance. Sila ang magiging recipient ng benefits in case of the insured’s passing.
For example: May life insurance si Juan with Php 1M death benefit in case of death. Beneficiary niya ang asawang si Maria. If Juan dies while covered by the policy, then Maria receives the Php 1M benefit.
Dependent. This often applies to health insurance. These are people nominated by the policyholder para makatanggap ng same protection under the policy.
Policy limit. Ang pre-agreed maximum amount na ibibigay ng insurer in case of accident or loss.
For example: You have health insurance with a Php 100,000 policy limit for dengue. Ito ang max amount na ire-reimburse ng insurer in case you get dengue.
Premium. Ang total cost na kailangan bayaran para ma-enforce ang policy. Usually, this is split into monthly payments. Ang premium ay determined ng insurer based sa amount of risk na nae-encounter ng insured.
For example: You have life insurance worth Php 100,000 na payable in the next 5 years (or 60 months). This means you need to pay Php 1,666.66 as monthly premium.
Oftentimes, kapag kinulang ang monthly budget, insurance is the first thing people stop paying for. However, pwedeng ma-cancel completely ang policy mo if you miss just one payment. This is why you should get insurance with the most affordable premium. For instance, GInsure offers dengue and COVID-19 insurance for as low as P39/month. It’s the lowest premium you’ll ever get.

Deductible. In case of accident or damage, ito ang initial amount na kailangang bayaran out-of-pocket ng policyholder. Once maabot ang maximum deductible, saka mae-enforce ang insurance coverage.
For example: May Php 5,000 deductible ka on your car insurance. Na-damage ang iyong kotse and you need Php 20,000 for repairs. Because of your deductible, the insurer will only cover Php 15,000.
Hindi lahat ng policies ay may deductible. This is often common sa property, car, o health insurance para pigilan ang insured na maging reckless. With a deductible, mas iingatan mo ang iyong asset. It’s because partly responsible ka sa pagbabayad in case of damages.
Kapag mas mataas ang deductible, mas mababa ang iyong monthly premiums.
Period of coverage. The length of time na covered ang insured ng policy. This can range from one year to the insured’s entire lifetime.
Riders. Additional conditions na pwedeng idagdag o ibawas sa initial policy to suit the insured’s needs.
Claim. Ang request ng policyholder to be compensated for expenses na covered ng insurance.
Ano-ano ang types of insurance?
Life insurance. Upon death of the insured, may ibinibigay itong death benefit sa beneficiaries. This is usually a single large payout known as lump sum payment. Life insurance has 2 kinds: term and whole life.
Term life. It only protects the insured for a limited time, usually 10-30 years.
Whole life. Lifelong protection para sa insured as long as nababayaran ang monthly premiums. After a certain period of time, pwede ring mag-loan o mag-withdraw from this policy.
Health insurance. Kino-cover at binabawasan nito ang eligible healthcare costs ng policyholder at kanyang dependents.
Depending on your health and budget, pwede kang kumuha ng full o partial coverage. An example of partial coverage is GInsure. Under GInsure, the Singlife Cash for Dengue Costs provides coverage from Dengue and COVID-19. Dahil specialized ito, GInsure offers it at a more affordable price. You can avail it sa GCash app for as low as Php 300/year.
Income protection insurance. This replaces the insured’s income kapag hindi sila makapagtrabaho due to an accident.
For example, ang Cash for Income Loss on Accidents ay nagbibigay ng monthly income replacement for 36 months. GInsure offers this insurance sa abot-kayang halaga. Depending on your age, premiums start at Php 836/year.
Car/Auto insurance. Binabawasan nito ang maintenance costs ng car owners in case of damage, vehicular accident, o theft.
Home insurance. Also known as property insurance. It covers the policyholder financially mula sa property damage na dala ng sakuna o aksidente.
Education insurance. It helps cover the insured’s education expenses para makatapos sila ng college.
How to apply

Anyone aged 18 and above can become a policyholder. However, pwede ring ma-insure ang minors, or gawing beneficiary o dependent.
I’m sold! Anong insurance ang dapat kong unahin?

If you’re just starting out, then get the insurance na pinakabagay sa iyong current situation. Lahat tayo ay at risk of financial loss dala ng pagkakasakit o pagkawala ng income. Therefore, you may need health or income protection insurance.
Moreover, laging i-compare ang iyong options. Iba-iba ang coverage, policy limit, riders, at service ng bawat insurer. Kung insurer na lang ang labanan, choose the one na madaling ma-contact for claims at may good service reputation. An example would be GInsure, which has the fastest insurance processing in PH. From buying insurance to filing a claim, lahat ng transactions ay magagawa sa GCash app.
As mentioned before, may mga policies na naka-cancel completely if you just miss one payment. To avoid this, read the fine print on every policy, lalo na regarding missed payments. Try to arrange an automatic payment option para ma-ensure ang regular payments.
Marami na ring products that bundle free insurance with a savings account, such as GSave. This is best kung nagsisimula ka pa lang sa iyong journey to financial freedom. Okay din ito kung gipit ka o hindi sigurado sa policy na nais kunin.

Lastly, it’s best na magpa-insure when you’re young. Insurance is generally cheaper kapag lower ang iyong level of risk. In your early twenties or thirties, you have less pre-existing conditions. Mas marami ka ring remaining years to pay your premium. In short, the longer you wait, the more expensive getting insured will be. So huwag nang mag-dalawang isip and get insured today!



